Molding Process
Accelerating Cycle Times for Medical Device Manufacturing
Efficient thermal management is crucial in the production of medical devices and drug delivery systems, where up to 80% of the injection molding cycle is consumed by cooling. This Atalys presentation at SPE/MPD's Minitec at MD&M West in Anaheim California introduces a robust methodology for designing cooling systems using steady-state response thermal models, aimed at significantly reducing cooling times and boosting manufacturing efficiency. By precisely quantifying cooling challenges and optimizing key design parameters, this approach provides a streamlined modeling strategy for rapid and effective analysis.
Optimizing Mold Cooling for Medical Plastics: Insights from a Leading Expert
In this exclusive interview, Dr. Crispino explores the science behind cure time optimization, advanced thermal management, and the latest cooling methods to ensure precision and efficiency in medical device manufacturing. Learn about innovative modeling techniques, materials analysis, and actionable insights that can transform your mold design process. Ideal for professionals in engineering, R&D, manufacturing, and procurement, this interview provides insights into how you can improve cycle times and product quality.
Major Design Rules for Plastic Injection Molding Medical Device Parts
Designing plastic parts for medical devices can be a complex and challenging process, especially when it comes to achieving tight tolerances, high precision, and optimal functionality. This guide explores the major design rules and provides tips and insights on how to optimize your part’s design for maximum efficiency and quality.
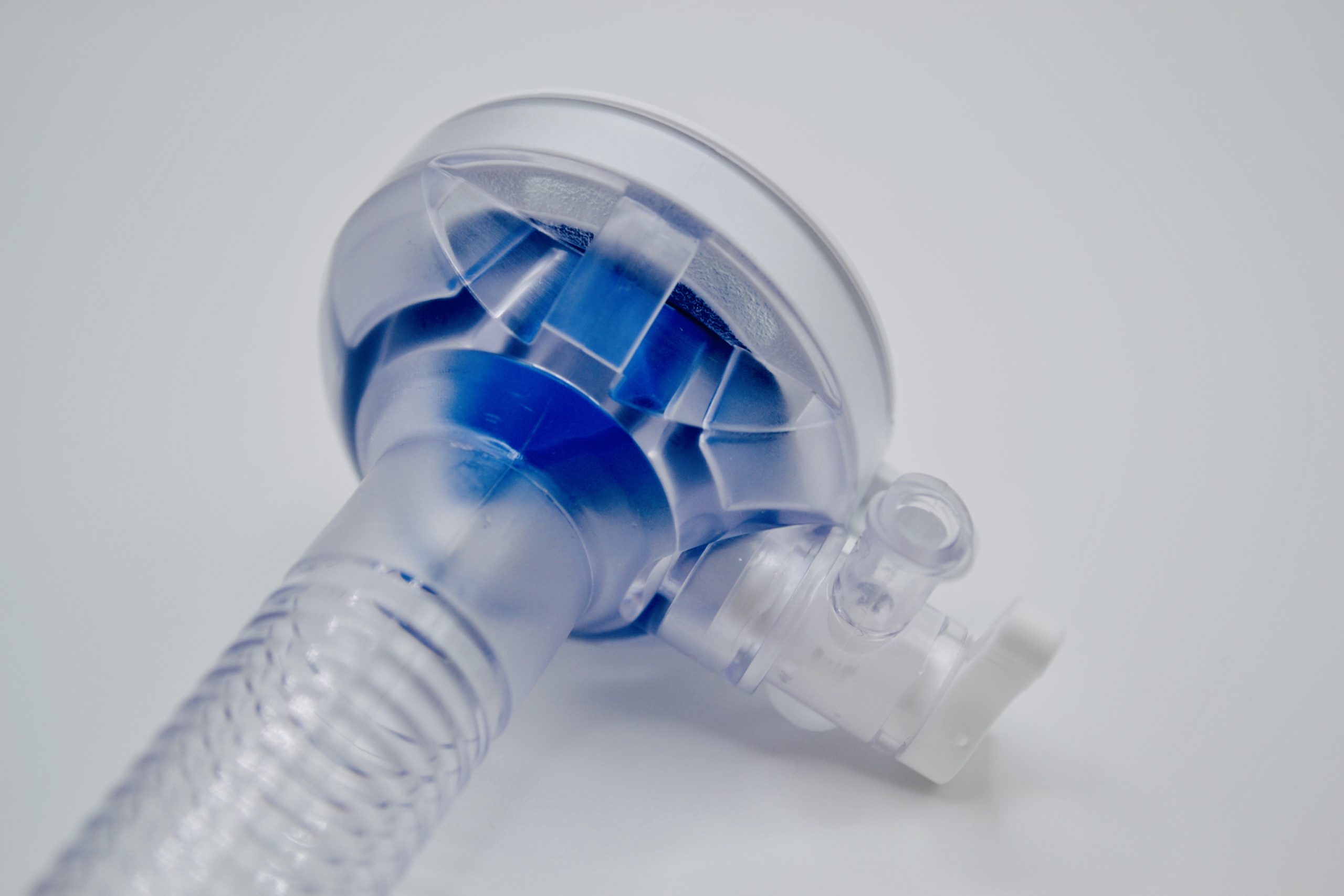
Molding No Draft Tubes
Medical device parts with cylindrical shapes are traditionally designed to have tapers in both internal and external walls which facilitate easy ejection of the molded part from the tool without any issues. There are times, however, when a part’s required tolerances and/or function will not allow for it. This was the case with a customer who wanted a tubular component molded without drafts under strict tolerances. Could the part be molded without any drafts? Find out in this case study.
How do you know if what you have is a tough cooling problem?
At Atalys, we have developed a method for estimating the optimum cure time for each molding assignment. In essence, the model allows us to quantify the cooling challenge to be overcome, and enables us to determine the key parameters of the mold design that would be necessary if the desired cure time is to be achieved. Download the white paper to learn more.
Long Cannula Cooling Challenge
A customer came to us with a cooling challenge involving a long cannula. The parts were coming off the press at high temperatures that rendered them unusable. As a short-term measure, the parts were kept longer in the mold to give them extra time to cool. This lengthened cycle times, however, and was far from sustainable. Find out how Atalys engineers came up up with a long-term, viable solution in this case study.